Choosing the right blockchain as a service platform comparison becomes critical as enterprises increasingly adopt distributed ledger technology for their business operations. The blockchain as a service (BaaS) market has evolved rapidly, offering businesses simplified access to blockchain infrastructure without the complexity of building and maintaining their own networks. Leading cloud providers and specialized blockchain companies now offer comprehensive BaaS solutions that enable organizations to deploy, manage, and scale blockchain applications efficiently.
Understanding the differences between various BaaS platforms helps organizations make informed decisions about their blockchain implementation strategy. Each platform offers unique features, pricing models, and integration capabilities that cater to different business requirements and technical specifications.
Blockchain as a Service Platform Comparison Fundamentals
Blockchain as a service represents a cloud-based offering that allows organizations to build, host, and operate their own blockchain applications and smart contracts on established blockchain infrastructure. This model eliminates the need for companies to invest in expensive hardware, hire specialized blockchain developers, or manage complex network operations.
The BaaS model follows similar principles to other cloud services, providing scalable infrastructure, managed services, and pay-as-you-use pricing models. Organizations can focus on developing their blockchain applications while leaving the underlying infrastructure management to experienced cloud providers.
Key benefits of BaaS platforms include reduced time-to-market, lower infrastructure costs, enhanced security through managed services, and access to enterprise-grade blockchain networks without significant upfront investments.
Core Components of BaaS Platforms
Modern BaaS platforms typically include several essential components that enable comprehensive blockchain development and deployment. Infrastructure management handles the underlying blockchain network operations, including node deployment, network monitoring, and automatic scaling based on demand.
Development tools and APIs provide developers with the necessary resources to build, test, and deploy blockchain applications. These tools often include integrated development environments (IDEs), testing frameworks, and debugging capabilities specifically designed for blockchain development.
Security and compliance features ensure that blockchain applications meet enterprise-grade security standards and regulatory requirements. This includes encryption, access controls, audit trails, and compliance reporting capabilities.
BaaS Deployment Models and Architecture
BaaS platforms offer various deployment models to accommodate different organizational requirements and security preferences. Public blockchain deployments utilize established networks like Ethereum or Bitcoin, providing maximum decentralization and network effects.
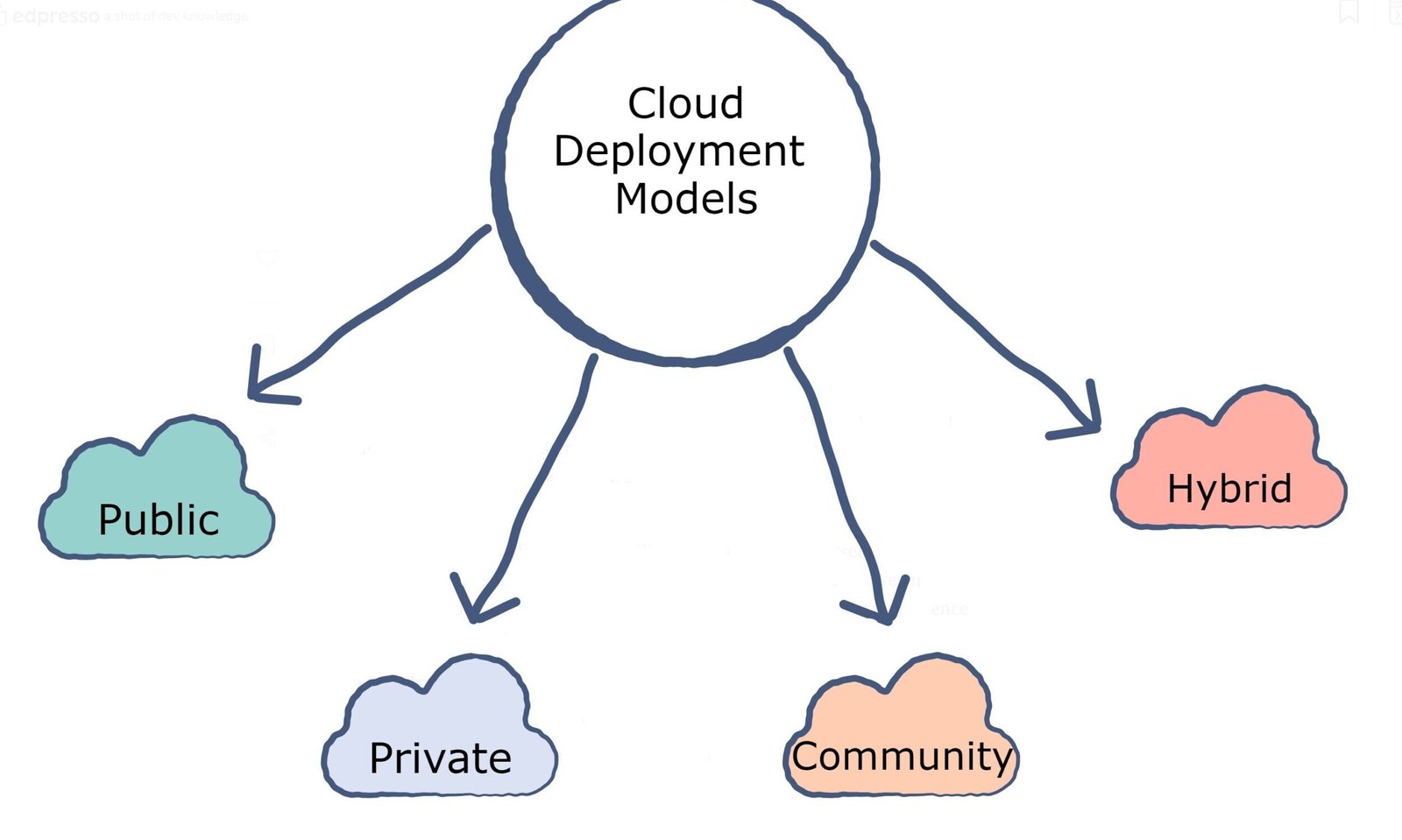
Private blockchain deployments create isolated networks for specific organizations or consortiums, offering enhanced control over network governance and data privacy. These deployments are particularly popular in highly regulated industries. Hybrid blockchain models combine elements of both public and private networks, allowing organizations to maintain sensitive data privately while leveraging public networks for certain operations like timestamping or verification.
Leading BaaS Providers: Comprehensive Platform Analysis
The BaaS marketplace features several major providers, each offering distinct advantages and specializations. Amazon Web Services (AWS) Blockchain provides managed blockchain services that support both Hyperledger Fabric and Ethereum networks, offering seamless integration with existing AWS infrastructure.
Microsoft Azure Blockchain Service focuses on consortium blockchain networks and provides pre-configured blockchain templates for rapid deployment. The platform emphasizes enterprise integration and includes comprehensive development tools.
IBM Blockchain Platform leverages Hyperledger Fabric technology and provides extensive enterprise features including governance tools, operational dashboards, and industry-specific solutions for supply chain, finance, and healthcare applications.
Amazon Web Services Blockchain Platform Features
AWS Blockchain offers two primary services: Amazon Managed Blockchain and Amazon Quantum Ledger Database (QLDB). Managed Blockchain supports popular open-source frameworks and handles network creation, member management, and certificate authority operations.
The platform provides automatic scaling capabilities that adjust network resources based on transaction volume and network demands. Integration with other AWS services enables organizations to build comprehensive blockchain applications using familiar cloud services.
Pricing models follow AWS’s pay-as-you-use philosophy, with charges based on network membership duration, peer node usage, and data storage requirements. This approach helps organizations manage costs while scaling their blockchain implementations.
Microsoft Azure Blockchain Service Capabilities
Azure Blockchain Service simplifies consortium network creation and management through pre-configured templates and automated governance features. The platform supports multiple blockchain protocols including Ethereum, Quorum, and Corda.
Development integration includes Visual Studio Code extensions, Azure DevOps pipelines, and comprehensive REST APIs that enable seamless application development workflows. The platform emphasizes developer productivity through familiar Microsoft development tools. Security features leverage Azure’s enterprise-grade security infrastructure, including Azure Active Directory integration, virtual network isolation, and comprehensive monitoring and logging capabilities.
IBM Blockchain Platform Enterprise Solutions
IBM Blockchain Platform provides a comprehensive enterprise blockchain solution built on Hyperledger Fabric. The platform offers flexible deployment options including cloud, on-premises, and hybrid configurations to meet diverse organizational requirements.
Operational tools include intuitive dashboards for network monitoring, member management, and transaction analysis. These tools enable non-technical users to oversee blockchain network operations effectively. Industry-specific solutions address common use cases in supply chain management, trade finance, food safety, and digital identity management. These pre-built solutions accelerate implementation timelines for organizations in specific verticals.
Technical Specifications and Performance Metrics
Evaluating BaaS platforms requires understanding key technical specifications and performance characteristics that impact application functionality and user experience. Transaction throughput capabilities vary significantly between platforms and blockchain protocols, affecting scalability for high-volume applications.
Consensus mechanisms implemented by different platforms influence transaction finality times, energy efficiency, and network security properties. Understanding these mechanisms helps organizations choose platforms aligned with their performance requirements.
Network latency and geographic distribution of nodes affect application responsiveness and user experience. Global organizations must consider data sovereignty requirements and regional compliance regulations when selecting BaaS providers.
Scalability and Performance Benchmarks
Transaction processing speeds represent critical performance metrics for enterprise blockchain applications. Hyperledger Fabric networks typically achieve 1,000-10,000 transactions per second depending on configuration and transaction complexity.
Ethereum-based BaaS solutions face throughput limitations of the underlying network but benefit from extensive developer ecosystems and interoperability with decentralized applications. Layer 2 scaling solutions are increasingly integrated into BaaS offerings to address these limitations.
Storage and data management capabilities impact applications requiring extensive data storage or complex queries. Some platforms provide integrated database solutions while others rely on external data storage systems.
Security Architecture and Compliance Features
Enterprise-grade security requirements drive many BaaS platform design decisions. Encryption at rest and in transit protects sensitive blockchain data throughout its lifecycle. Hardware security modules (HSMs) provide additional protection for cryptographic keys and sensitive operations.
Identity and access management systems ensure that only authorized users can access blockchain networks and perform specific operations. Integration with existing enterprise identity systems simplifies user management and maintains security policies.
Compliance certifications including SOC 2, ISO 27001, and industry-specific standards demonstrate platform readiness for regulated environments. Audit trail capabilities provide comprehensive logging for regulatory reporting requirements.
Pricing Models and Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
BaaS pricing structures helps organizations budget effectively for blockchain implementations. Most providers offer multiple pricing tiers based on network size, transaction volume, and feature requirements. Infrastructure costs typically include charges for network membership, peer nodes, ordering services, and data storage. These components scale with network usage and provide flexibility for growing blockchain applications.
Additional costs may include development tools, premium support services, professional services for implementation assistance, and third-party integrations. Organizations should evaluate total cost of ownership over multi-year periods when comparing platforms.
Cost Optimization Strategies for BaaS Deployments
Right-sizing blockchain networks helps organizations balance performance requirements with cost considerations. Starting with smaller configurations and scaling based on actual usage patterns prevents over-provisioning. eserved capacity pricing options offered by some providers can significantly reduce costs for predictable workloads.

Organizations with steady-state blockchain operations benefit from committing to longer-term capacity reservations. Multi-cloud strategies may provide cost optimization opportunities by leveraging competitive pricing and avoiding vendor lock-in. However, these approaches require additional complexity in network management and integration.
ROI Calculation Framework for Blockchain Projects
Measuring return on investment for blockchain implementations requires considering both quantitative and qualitative benefits. Cost savings from process automation, reduced intermediaries, and improved efficiency provide measurable financial benefits.
Risk reduction through enhanced transparency, immutable audit trails, and automated compliance checking provides value that may be difficult to quantify but significantly impacts business operations. Time-to-value considerations include implementation timelines, developer productivity improvements, and faster deployment cycles enabled by managed BaaS platforms compared to building blockchain infrastructure from scratch.
Integration Capabilities and Ecosystem Support
Modern enterprises require blockchain platforms that integrate seamlessly with existing systems and support extensive third-party ecosystems. API compatibility and standardization facilitate integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, and other business applications.
Middleware and integration platforms provide pre-built connectors for common enterprise systems, reducing development time and complexity. These solutions often include data transformation capabilities and error handling mechanisms.
Developer ecosystem support includes comprehensive documentation, community forums, training resources, and professional services. Strong ecosystems accelerate development and provide ongoing support for blockchain implementations.
Enterprise System Integration Patterns
Common integration patterns include event-driven architectures that trigger blockchain transactions based on business events in existing systems. These patterns maintain data consistency across hybrid environments combining traditional databases and blockchain networks.
Message queuing systems provide reliable communication between blockchain networks and enterprise applications, ensuring transaction delivery and handling system outages gracefully. API gateway solutions manage access to blockchain networks from multiple applications while providing security, rate limiting, and monitoring capabilities. These gateways simplify blockchain integration for application developers.
Third-Party Tool and Service Compatibility
Analytics and monitoring tools provide insights into blockchain network performance, transaction patterns, and business metrics. Integration with existing business intelligence platforms enables comprehensive reporting across traditional and blockchain data sources.
Development framework compatibility ensures that existing developer skills and toolchains remain relevant for blockchain application development. Platforms supporting popular programming languages and development methodologies reduce learning curves. Marketplace ecosystems provide access to pre-built smart contracts, industry-specific solutions, and specialized services. These marketplaces accelerate development by providing proven components and reducing custom development requirements.
Industry-Specific Use Cases and Success Stories
Different industries leverage BaaS platforms for specific use cases that align with their business requirements and regulatory environments. Supply chain management applications track product provenance, verify authenticity, and ensure compliance with quality standards.
Financial services utilize blockchain for trade finance, cross-border payments, and regulatory reporting. These applications benefit from immutable transaction records and automated compliance checking through smart contracts. Healthcare organizations implement blockchain solutions for secure patient data sharing, pharmaceutical supply chain verification, and medical research data management while maintaining HIPAA compliance.
Supply Chain and Logistics Applications
Global supply chains benefit from blockchain-enabled traceability that provides end-to-end visibility into product journeys from raw materials to end consumers. This transparency helps identify and resolve quality issues quickly while building consumer trust.
Sustainability tracking applications monitor environmental impact metrics throughout supply chains, enabling companies to verify and communicate their environmental commitments. Blockchain immutability ensures data integrity for sustainability reporting.
Counterfeit prevention systems use blockchain verification to authenticate products and detect unauthorized copies. These systems particularly benefit luxury goods, pharmaceuticals, and other high-value products vulnerable to counterfeiting.
Financial Services and Fintech Innovations
Trade finance digitization reduces processing times from weeks to days by automating document verification and streamlining approval workflows. Smart contracts execute payments automatically when predefined conditions are met. Cross-border payment solutions leverage blockchain networks to reduce settlement times and eliminate intermediate banks. These solutions particularly benefit remittances and international trade transactions. Regulatory reporting applications automatically collect and verify transaction data for compliance submissions. Immutable audit trails simplify regulatory examinations and reduce compliance costs.
Implementation Methodology and Best Practices
Successful BaaS implementation requires structured methodologies that address technical, organizational, and governance considerations. Pilot project approaches allow organizations to gain experience with blockchain technology while limiting initial investment and risk.
Stakeholder engagement across business units, IT departments, and external partners ensures alignment on objectives, requirements, and success metrics. Change management programs address cultural and process changes required for blockchain adoption. Governance frameworks establish decision-making processes, network membership criteria, and operational procedures for ongoing blockchain network management. These frameworks become particularly important for consortium networks involving multiple organizations.
Project Planning and Requirements Analysis
Requirements gathering should address functional needs, performance expectations, security requirements, and compliance obligations. Technical requirements include integration points, data migration needs, and infrastructure constraints.
Risk assessment identifies potential challenges including technical limitations, regulatory uncertainties, and organizational change management requirements. Mitigation strategies should address identified risks before implementation begins.
Success metrics definition provides measurable criteria for evaluating project outcomes. These metrics should include both technical performance indicators and business value measurements.
Development and Deployment Strategies
Agile development methodologies work well for blockchain projects due to the evolving nature of technology and requirements. Iterative development allows for course corrections based on stakeholder feedback and technical discoveries. Testing strategies must address blockchain-specific considerations, including consensus mechanism behavior, smart contract logic, and network performance under various load conditions. Automated testing frameworks accelerate development cycles. Deployment planning considers network configuration, member onboarding, data migration, and cutover procedures. Phased deployment approaches reduce risk by gradually transitioning operations to blockchain networks.
Conclusion
Conducting a thorough blockchain as a service platform comparison enables organizations to select the optimal solution for their specific requirements and constraints. The BaaS landscape continues evolving with new features, improved performance, and expanded ecosystem support from major cloud providers and specialized blockchain companies.
Success with BaaS implementations requires careful evaluation of technical capabilities, cost structures, integration requirements, and long-term strategic alignment. Organizations should pilot selected platforms with small-scale projects before committing to large-scale implementations.
See More : Best Cryptocurrency Trading Platform 2025 Top 10 Exchanges Reviewed

